rrimyuu 님의 블로그
Paper review | A Multimodal Ensemble Deep Learning Model for Functional Outcome Prognosis of Stroke Patients 본문
Paper review | A Multimodal Ensemble Deep Learning Model for Functional Outcome Prognosis of Stroke Patients
rrimyuu 2024. 7. 8. 16:56Introduction
acute ischemic stroke 은 clinical aspects such as age, patient characteristics, cognition, treatment, comorbidities, stroke severity, and even imaging biomarkers 영향으로 인해 functional outcomes 예측이 어려움. 최근 machine learning 과 deep learning 으로 인해 성능이 매우 향상되었지만 주로 clinical data 에 의존하며 AIS 를 예측하는 데 중요한 정보가 담긴 영상 데이터 (the extent of tissue damage, penumbra*, and collateral circulation) 를 통합하지 않음.
따라서, 본 연구에서는 comprehensive model 을 사용하여 AIS patients 의 long-term functional outcomes 를 예측하려 함. 제안하는 모델은 다기관 MR 스캔 및 임상 데이터를 결합함. ensemble model 은 성능 향상, 편향 최소화 및 예측 결과 변동을 감소시킴. interpretability method 를 사용해서 decision making process 를 시각화함.
* penumbra: 실질적인 뇌 조직 손상이 일어나기 전에 주변 조직이 아직 회복될 가능성이 있는 영역을 나타냄. 이 지역에서는 혈액 공급이 일시적으로 차단되었지만, 뇌 조직이 아직 완전히 손상되지 않았기 때문에 재관류 치료 등의 조치를 통해 회복될 수 있음.

Method
Data collection
- Data were obtained from the Korean Stroke Neuroimaging Initiative (KOSNI) Registry, a prospective observational study conducted at 18 tertiary stroke centers in South Korea over an 8-year period (2011–2018).
- Of the 5,018 patients, 2,606 were eligible. Among the patients, 1,613 (61.90%) exhibited an mRS of 0–2, whereas 993 (38.10%) achieved an mRS of 3–6 at 90 days post-stroke.

Image data preprocessing
- Baseline MR encompassed two subtypes of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI): DWI with a b-value of 1,000 s/mm2 (b1000) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map, and fluid-ttenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR).
- Data pre-processing for raw MR scans
- N4 bias field correction - MRI 스캔 데이터에는 편향된 강도가 있을 수 있습니다. N4 바이어스 필드 보정은 이러한 편향을 제거하는 기술입니다. 이를 통해 각 MRI 모드에서 발생할 수 있는 밝기 불균형을 보정합니다.
- Skull stripping using a brain mask derived by K-means clustering - 두 번째 단계는 두뇌 외곽부를 제거하는 것입니다. K-means 클러스터링을 사용하여 얻은 두뇌 마스크를 기반으로 두뇌 외곽을 제거하여 뇌 조직만을 남기는 작업입니다. 이는 뇌 영역 외의 데이터를 제거하고 정확한 분석을 가능하게 합니다.
- DWI images (b1000 and ADC map) alignment to MNI 152 space using ANTs SyN registration algorithm - DWI (Diffusion Weighted Imaging) 이미지는 MNI 152 공간에 2mm 이동 등 방법을 사용해 정렬합니다. The voxel intensity values in each image were normalized to ensure they fell within the range of 0–1.

- neuroimaging normalization guide : https://www.nitrc.org/docman/view.php/881/1853/Manual%20(version%208/8/2014)
>> matlab SPM 으로 하는 듯 . (?) 위 단계들 모두 가능한지 테스트해보기.
Clinical data preprocessing
The clinical variables comprised 22 demographic and clinical features: age; sex; previous history of hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia and stroke (including TIAs); current smoking status; body mass index (BMI); systolic blood pressure; diastolic blood pressure (DBP); hematocrit level; hemoglobin level; blood glucose level; creatinine level; total cholesterol level; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C); low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; total National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) [8] at admission; duration between stroke onset and admission; reperfusion therapy status; risk status of cardiac embolic sources; and Trial of ORG 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) [26] subtypes, including large-artery atherosclerosis, cardioembolism, small-vessel occlusion, other determined etiology, and undetermined etiology.
Proposed approach
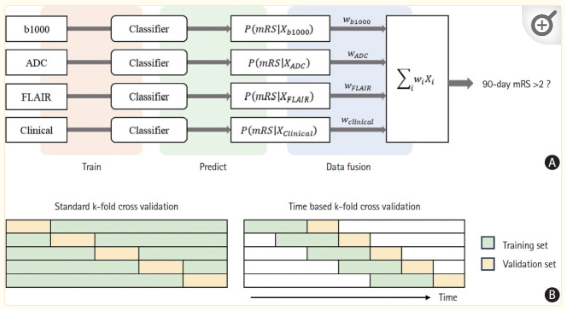
- For the clinical data, we employed a simple, fully connected neural network (FCN) consisting of three layers with eight hidden units. This FCN was trained using the Adam optimizer and dropout regularization was applied to prevent overfitting.
- we used the 3D implementation version of ResNeXt to extract features from the entire MR image. To enhance the performance, we incorporated the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) after each ResNeXt block.
>> the channel attention module and the spatial attention module - Following ResNeXt-CBAM, the extracted features comprised 2,048 nodes for the final classification. Class probability was obtained using the sigmoid function for the dichotomized mRS.
- To ensure fast convergence and robust training, we used the Rectified Adam optimizer with cosine-annealing learning rate scheduling.
- To prevent overfitting, additional strategies were employed, including early stopping and RandAugment, a stochastic automated data augmentation method that applies several transformation methods.
Data fusion between baseline models
To improve model performance, we employed a data-fusion technique using a weighted average method. This approach combines probability vectors obtained from each model. The weights for the fusion were determined using the differential evolution method by optimizing the maximum F1 value of the ensemble model.
Evaluation
- We employed two distinct approaches for model training and evaluation: standard k-fold cross-validation (CV) and time-based k-fold CV
>> In the standard approach, a stratified 5-fold CV was used to maintain consistent proportions of output classes in each fold. In contrast, time-based k-fold CV adopts sliding window CV, a resampling technique used to manage time-series data. - We assessed the performance of the models by measuring sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value, F1 score, and area under the curve (AUC).
>> we conducted a DeLong test to identify any statistically significant differences based on the models trained on the entire training dataset. The significance level for statistical tests was set at P<0.05. We further calculated 95% confidence intervals (CI) using 200 bootstrap samples. - For the clinical data model, we used the kernel Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP) to estimate the contribution of each input feature.
- For the imaging data, we used Grad-CAM to visualize significant brain regions and classify mRS outcomes.
>> Grad-CAM-derived ROI-to-brain anatomy mapping was analyzed using the AtlasQuery tool of the FMRIB Software Library based on the MNI structural atlas, Harvard–Oxford cortical structural atlas, and Harvard–Oxford subcortical structural atlas.
Results
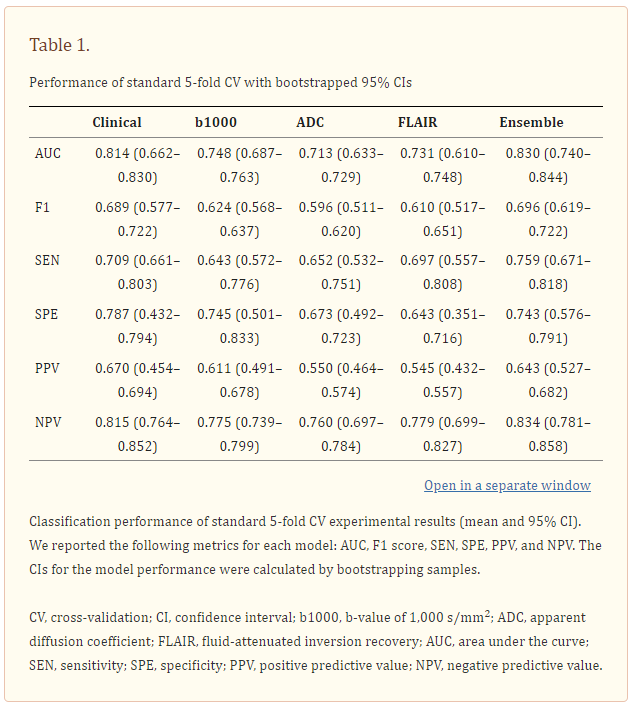
Prediction performance

Interpretable model analysis

Discussion
- 앙상블 모델이 가장 높은 평균 성능을 달성했지만, 임상 데이터만을 사용한 모델도 좋은 성능을 보였음. 그러나 임상 데이터의 data drift 에 대한 취약성을 인식하는 것이 중요함. 다기관 데이터 소스를 사용했음에도 불구하고 AUC의 95% 신뢰 구간이 0.662에서 0.830까지 넓게 분포한 바 있음. 반면, 앙상블 모델은 훈련 및 테스트 세트 간의 데이터 분포 차이에 의해 발생하는 성능 변동을 효과적으로 완화하며 견고한 성능을 보였음. 이러한 안정성은 병원이나 영상 시설 간의 변동이 있는 실제 임상 환경에서 앙상블 모델이 특히 유리함을 나타냄.
- 입력 데이터와 기능적 예후 불량 사이의 관계를 탐구하기 위해, 우리는 각 임상 및 영상 입력에 대해 SHAP 및 Grad-CAM을 사용한 시각적 분석을 수행함.
- SHAP 플롯은 임상 데이터에 기반한 기능적 예후 예측에 있어 나이와 NIHSS 점수가 중요한 영향을 미친다는 것을 보여주었으며, 이는 이전 연구들과 일치함.
- Grad-CAM은 모델이 집중하는 뇌 영역을 보여주기 위해 사용되었음. 흥미롭게도, 평균 Grad-CAM 그래프는 전체 병변이 아닌 특정 뇌 영역을 포함했는데, 이러한 결과는 불량한 기능적 예후가 좌측 소뇌와 측두-후두부 영역과 상관관계가 있음을 시사함.
>> 뇌졸중 기능적 예후는 운동 기능, 균형, 시각 기능에 영향을 받는 일상 활동의 장애 또는 의존 수준을 평가하는 mRS를 사용하여 평가되었음. NIHSS는 운동 기능에 비해 운동 실조 및 시각 기능에 적은 점수를 부여함.
>> 따라서, 나이와 NIHSS 점수라는 중요한 임상적 요소를 고려할 때, 균형 조절 (banlance control) 을 담당하는 소뇌 ( cerebellum) 와 시각 경로 (optic pathway) 를 포함하는 측두-후두부 피질 (temporo–occipital cortex) 이 불리한 예후와 관련이 있을 수 있음. which houses the optic pathway, may have been associated with unfavorable outcomes.
Limitations
- 본 앙상블 모델은 MR 영상에 의존했고 뇌졸중 진단에 CT 기반 영상을 사용하는 많은 기관들이 사용하기 적합하지 않음.
- 연구 대상은 뇌졸중 발병 후 24시간 이내 뇌졸중 센터를 방문한 환자로 구성. 평균 입원 NIHSS 점수가 5점으로 높은 중증도를 보였음. 이러한 중증도 불일치는 모델의 일반화를 제한할 수 있음.
- 완전한 병변 성장 ( full lesion growth) 이 없음. MR 영상 대부분이 초기 기준 영상 (early baseline images) 이었음.
- 실제 데이터는 시간 경과에 따른 분포 및 소스 변화로 인한 data drift 가 나타나는 경우가 있으므로 실제 환경에서 추가적인 검증이 필요함.
- 과적합을 완화하고자 RandAugment 및 early stopping 을 사용하였지만 데이터 세트 크기는 제한적이었음. 추후 큰 외부 데이터 세트를 통한 성능 개선 및 과적합 완화가 필요함.
- 모델이 ROI 에 더 집중하고 정확한 특징을 추출할 수 있도록 주의 메커니즘을 사용했음. (attention mechanism) 하지만 일부 이미지에서는 여전히 병변 크기와 위치의 차이로 인한 노이즈가 발생함. 향후 연구에선 이러한 노이즈를 필터링하여 모델 성능 개선이 포함되어야 함.




