rrimyuu 님의 블로그
Paper review | Numerical study of hemodynamic changes in the Circle of Willis after stenosis of the internal carotid artery 본문
Paper review | Numerical study of hemodynamic changes in the Circle of Willis after stenosis of the internal carotid artery
rrimyuu 2024. 7. 2. 16:271. Introduction
(요약) ischemic stroke 을 앓는 많은 환자들이 circle of willis (CoW) 협착과 함께 internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis 를 보임. carotid artery stenosis, CoW atherosclerosis 는 뇌혈류 보상 저하 (cerebral blood flow decompensation*) 를 유발하고 ischemic stroke 발병을 촉진함. 두 부위 모두에서 stenosis 가 발생하는 이유는 알 수 없음. 따라서 이 연구에서는 ICA stenosis 가 CoW 에 미치는 혈역학적 효과를 조사함.
* cerebral blood flow decompensation : 뇌의 혈류가 갑자기 악화되는 상태를 의미. 일반적으로 뇌의 혈액 공급이 감소하거나 막힘이 발생하여 뇌 조직에 산소와 영양 공급이 충분하지 않을 때 발생할 수 있음.
혈액을 공급하는 동맥이 협착되거나 폐쇄되면 CoW 구조를 통해 혈액 재분배 및 보상을 어느 정도 조절하여 뇌 활동을 유지하는 데 도움이 될 수 있음. 개통되어 있는 CoW 에 비해 CoW 에 변화가 생긴 경우 ischemic stroke 발생 가능성이 38% 더 높음. 따라서 CoW 의 뇌혈류 보상은 ischemic stroke 에 중요한 역할을 함. ICA stenosis 와 함께 CoW stenosis 를 동반한 환자가 임상적으로 많이 나타남. ICA stenosis 는 CoW 혈역학적 환경을 변화시켜 CoW 내부에서 stenosis 을 발생시킬 수 있음. 이렇게 되면 CoW 재분배 능력이 제한되어 ischemic stroke 이 발생할 수 있음.
※ 혈역학적 관점에서 CoW 에서 협착이 발생하는 이유
내막 과성증(intimal hyperplasia, IH)은 경화성 혈전 형성 (sclerotic plaque formation) 의 중요한 원인임. IH는 혈관 내피세포의 손상이나 기능 저하에 대응하여 혈관 매끄러운 근육 세포들이 지속적으로 비정상적으로 침투하고 과도하게 증식하는 현상임. IH를 일으키는 다양한 요인 중에서 혈역학적 요인이 상당히 중요하게 작용하는 데 그 중 가장 중요한 혈역학적 요인으로는 벽 전단 응력 (Wall Shear Stress, WSS) 과 진동 전단 지수 (Oscillatory Shear Index, OSI) 가 있음.

1) WSS : 혈류에 의해 동맥 벽에 작용하는 접선 응력으로 내피 표면 (endothelial surface*) 에 중대한 영향을 미치는 주요한 요소임. 생리적인 WSS는 내피 기능을 조절함. 낮은 WSS (<1 Pa) 는 죽상동맥경화반 (atherosclerotic plaques) 발달을 촉진할 수 있음. 내피 기능에 영향을 미치는 것은 일시적인 WSS 가 아니라 장시간 노출되는 WSS 환경이므로 time-averaged wall shear stress (TAWSS) 으로 표현할 수 있음.

* endothelial surface : 혈관 내부를 덮고 있는 가장 안쪽의 세포층을 의미함. 이 세포층은 혈관 내벽을 통해 혈류와 직접 접촉하며, 혈액과 상호작용하면서 중요한 생리적 기능을 수행함. 혈관 내피 세포는 혈관의 구조적 유지뿐만 아니라 혈액의 응집 방지, 염증 반응 조절, 혈관 성장 및 회복에 관여하는 등 여러 가지 기능을 수행함.
2) OSI : OSI 는 혈류 불안정성을 나타내는 기계적인 지표임. 높은 OSI 는 WSS 보다 죽상동맥경화증 (atherosclerosis) 와 취약 혈전 형성의 조기 징후임. 진동성 역류 (oscillatory reflux) 에 장기간 노출되면 혈관 내피에 매우 부적합하며 혈전 형성 가능성이 높음. 낮은 OSI 는 덜 방해 받는 혈류 상태를 의미하므로 IH 형성에 불리하고 죽상동맥경화증 위험을 회피하는 데 도움.
>> 임상에서 뇌동맥 (cerebral arteries) 의 국소적인 혈역학적 변화를 얻는 데 어려움이 있어 CFD 기술을 사용하여 혈역학적 변화를 수치적으로 계산함. 따라서, 본 연구에서는 ICA stenosis 변화가 CoW 의 TAWSS, OSI 에 미치는 영향을 조사하기 위해 뇌동맥 3D/0D 기하학적 다중척도 모델 (geometric multiscale model) 을 개발하는 것임.
2. Materials and mathods
2.1. The establishment of cerebral geometric multi-scale model
1) The 3D model reconstruction
- based on computed tomography angiography (CTA) images of the cerebral artery of two volunteers provided by Peking University Third Hospital.
- (Volunteer 1) the anatomical structure of the CoW was missing the P1 segment of the right posterior cerebral artery (우측 후두동맥).
- (Volunteer 2) the anatomical structures of the CoW was missing the left posterior communicating artery (좌측 후방연락동맥).

- (software) Freeform 사용하여 혈역학적 계산을 위한 두 모델을 기반으로 경미/중간/심각 수준의 우측/좌측 내경동맥 협착을 구현함.
- (NASCET) severity of stenosis 계산함.
- (The 3D model hemodynamic calculation) the Navier-Stokes equations
2) lumped parameter modeling
- 회로 소자를 활용하여 혈액 순환계를 시뮬레이션 하는 일반적인 방법. 전신 시뮬레이션 (the systemic simulation) 을 위한 완전 폐루프 0D 모델 (closed-loop 0D model) 이 확립되었음. C는 정전용량 (capacitance), L 은 inductor, R 은 resistance, dt 은 time step.
- This model had 6 artery units, 6 vein units, 4 peripheral circulation units, 6 cerebral microcirculation units and a cardiopulmonary circulation unit, for a total of 23 units. (각 회로 소자 매개변수는 임상적인 측정과 일치하도록 조정)
- Closed-loop lumped parameter model of the blood circulatory system where F is for arterial units, H is for venous units, and G is for peripheral circulation units.

3) the coupling interface of the gemoetric multiscale model of the cerebral arteries
- 뇌동맥의 기하학적 다중 척도 모델 (the geometric multiscale model of the cerebral arteries) 의 확립은 0D, 3D 모델을 기반으로 함. 다중 척도 모델의 커플링 인터페이스 (the coupling interface) 는 공급 동맥 (the feeding arteries, ICA & BA) 와 뇌 미세순환 (brain microcirculation) 과 일치하도록 설계되었음. 본 연구에서는 아래 그림과 같이 0D/3D coupling alogrithm 을 사용하여 초기 조건을 설정하고 다중 척도 모델을 해결함.
- 3D 모델에 의해 계산된 입구 압력 (inlet pressure) 과 출구 유량 (outlet flow) 은 0D 모델에 의해 계산된 경계 조건임. 0D 모델의 입구 유량 (inlet flow) 과 출구 압력 (outlet pressure) 은 3D 모델의 경계 조건. 데이터 상호작용은 each 3D calculation time step 마다 한 번씩 수행되면서 잔여 감지 항목 (residual detection items) 도 동시에 수행됨. the residual 이 목표값보다 작을 경우 시뮬레이션을 종료함.
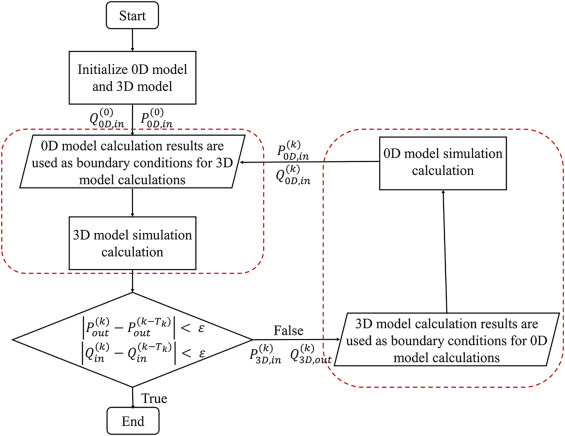
2.2. Hemodynamic calculation of the geometric multi-scale model
1) Parameters and equations of the 3D model
- (software) ANSYS-CFX
- Fluid density was 1050 kg/m3, viscosity was 0.0035 Pa/s, the vessel wall was simplified to a rigid wall, and blood flow was transient.
- The number of mesh elements for each cerebral artery model was 3,167,804 ± 61,131.
- Pulsating blood flow in the cerebral artery is a transient incompressible Newtonian fluid flow problem.
- The Navier–Stokes equations were applied for hemodynamic simulations of the 3D model, and the flow was assumed to be laminar.
2) Hemodynamic calculation of the 3D model
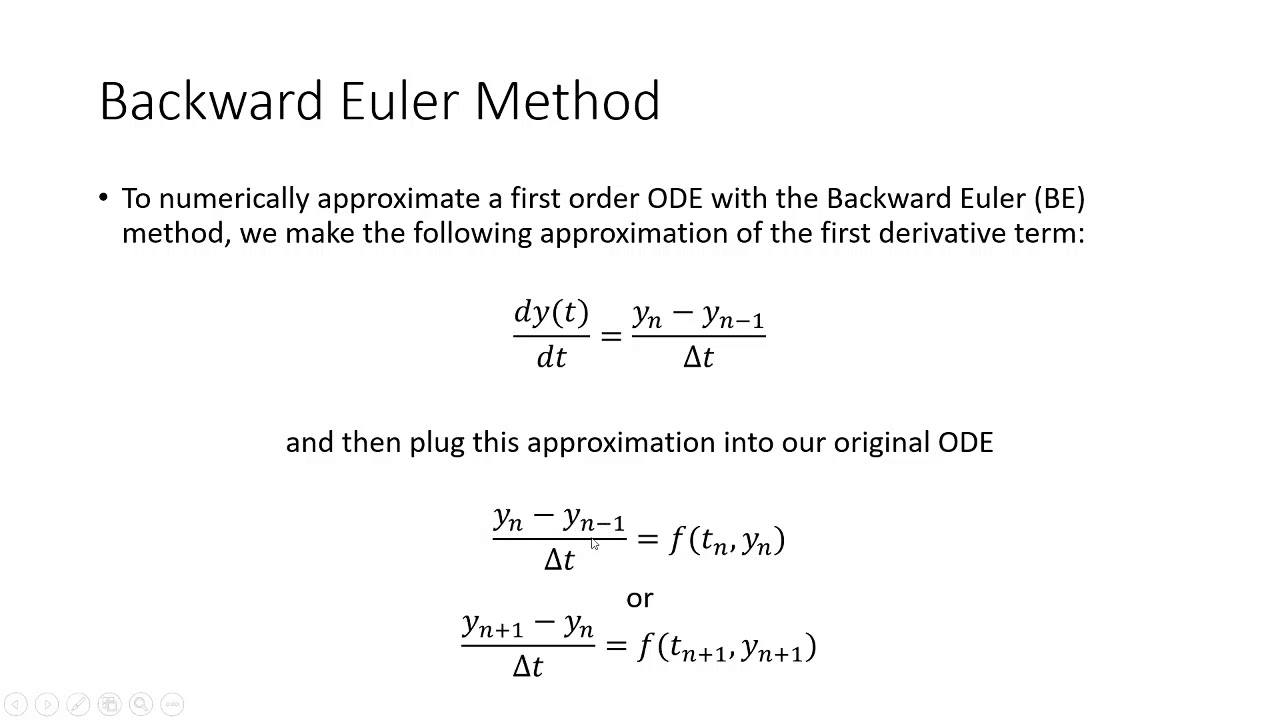
- Discretization in time* was based on a second-order backward Euler method and an implicit scheme.
- During multiscale calculation the time step of the 3D model was 1 ms, while the time step of the 0D model was 0.01 ms. The two models undertook a data exchange after every 100 calculations of the 0D model.
- The continuous computational domain (실제 물리적 시스템이나 현상을 모사하고자 하는 공간을 의미함. 이 연구에선 뇌동맥 모델링) was divided into finite sets of discrete points, which were mesh nodes, while discretization in space was based on divided mesh nodes. (메시 노드로 구성되어 있다?)
- The differential equations (미분 방정식**) and their solutions (해) on these mesh nodes were transformed into corresponding algebraic equations (대수 방정식***), meaning that discrete equations (이산 방정식****) were established.
- Discrete equations were solved, and the solution on each node was acquired. (이산 방정식을 해결하고 각 노드에서 해를 구함)
- In addition, the solution between nodes was assumed to vary smoothly, and so an interpolation method was used to obtain approximate solutions for the entire computational domain. (노드 사이의 해는 부드럽게 변화한다고 가정하므로 근사 솔루션을 얻기 위한 보간 방법을 적용함.)
* Discretization in time : 연속적인 시간을 일정한 간격으로 나누어서, 수치적으로 해결할 수 있는 형태로 변환하는 과정을 말함. 시간을 여러 개의 작은 단계로 나누어 각 단계에서 시스템의 상태를 계산함. 이 때, 각 단계를 시간 단계(time step)라고 하며, 이 시간 단계 안에서 시스템의 상태를 업데이트하고 새로운 시점에서의 상태를 계산함.
** 미분 방정식 (differential equation) : 함수의 도함수들 사이의 관계를 나타내는 방정식으로 물리적인 현상이나 자연 현상에서 공간에 따른 변화를 설명할 때 주로 사용됨.
*** 대수 방정식 (algebraic equation) : 변수들 사이의 관계를 나타내는 방정식임. (ex. 2x+3y = 10 -> x와 y 사이의 관계를 표현)
**** 이산 방정식 (discrete equation) : 연속적인 함수를 일정한 구간으로 나누어 이산적인 점에서만 정의된 방정식임. 일반적으로 시간이나 공간을 여러 개 작은 구간으로 나누어서 모델링할 때 사용됨.
- The 0D model was compiled into ANSYS-CFX through User Routines to couple with the 3D model.
- A function to simulate the ventricular contraction was applied to the variable capacitance CLV(t) and CRV(t) of the left and right ventricles in Fig. 1 (Panel II) to provide an energy source for the entire circulatory system.


* Double Hill function : 생리학적이나 생화학적 현상을 모델링하는 데 사용되는 수학적 함수임. 이 함수는 Hill 함수의 개념을 확장하여 두 개의 입력 변수를 동시에 처리할 수 있음.
2.3. Model validation
- This study utilized transcranial Doppler (TCD) to obtain the common carotid artery (CCA) and basilar artery (BA) flow velocities in two volunteers. The frequency of the probe was adjusted to 4.0-12.0 MHz, and the probe was directed towards the CCA and the basilar artery of the subjects, respectively, to measure their internal diameter and average flow velocity.
- ICA flow 는 CCA flow 의 80% 라는 이론을 통해 간접적으로 얻음 .
>> TCD를 이용한 two volunteers 의 CCA, BA 혈류 속도 (v) 측정 결과는 two volunteers 의 해부학을 기반으로 한 3D/0D the geometric multiscale modeling 의 계산 결과와 비교되었음.

2.4. Relevant hemodynamic indicators

3. Results
3.1. Cerebral model verification
Table 1 shows the flows in the left and right internal carotid arteries and basilar arteries in two volunteers (without ICA stenosis) under normal conditions based on TCD measurement. The calculation results from the 3D/0D geometric multi-scale models established in this study are consistent with the clinical measurement results for the two volunteers, with a MSE of 2.2 %, which is within a reasonable range.

3.2. Hemodynamic effects of different ICA stenosis severities on the CoW
CoW 의 혈역학적 환경 변화를 조사하기 위해 다양한 ICA stenosis 를 모델링함.
3.2.1. TAWSS
- 정상 조건에서 CoW 의 TAWSS 는 모두 정상 범위 (1-7 Pa) 내 있었으나 좌우 내경동맥 (ICA) 협착 심각도를 조정하니 TAWSS 가 다르게 변화하는 것으로 나타남.
- (Volunteer 1) Moderate stenosis 수준에서 LICA Stenosis 에선 낮은 TAWSS (0.973 Pa) 보이는 혈역학적 환경으로 변화. 낮은 TAWSS (< 1 Pa) 해당하는 면적은 the surface area of the left posterior communicating artery 의 82.9% 을 차지했음.
- (Volunteer 1) Moderate stenosis 수준에서 RICA Stenosis 에선 낮은 TAWSS (0.893 Pa) 보이는 혈역학적 환경으로 변화. 낮은 TAWSS (< 1 Pa) 해당하는 면적은 the surface area of the A1 segment of the right anterior cerebral artery 의 76.58% 을 차지했음.

3.2.2. OSI
- 정상 조건에서 CoW 의 OSI 는 모두 정상 범위 (<0.2) 내 있었으나 좌우 내경동맥 (ICA) 협착 심각도를 조정하니 OSI 가 다르게 변화하는 것으로 나타남.


4. Discussion
- 뇌혈류 보상은 허혈성 뇌졸중 발생에 핵심적인 역할을 함. CoW 는 뇌혈류 보상에 중요한 경로임. 뇌혈류 보상은 CoW 형태뿐만 아니라 CoW 내 죽상경화성 병변 존재 여부에 영향을 미침. 낮은 TAWSS, 높은 OSI는 죽상경화성 병변을 촉진함. ICA 협착으로 인한 CoW 내 혈역학적 환경 변화를 조사하고자 했음.
4.1. Cerebral model verification analysis
이 폐쇄루프 기하학적 다중척도 모델의 장점은 심장 모듈에서 전체 시스템에 전원을 제공하고 인체의 전체 혈류 순환 시스템의 운영 상태를 시뮬레이션할 수 있다는 점입니다. 인체의 혈류 순환 시스템은 병렬 회로 시스템과 유사하며, 3D 모델에서 혈류 저항을 증가시키는 내경동맥 경도증이 발생할 경우 해당 부분의 혈류가 적응적으로 감소하고 다른 분기에서 혈류가 증가할 것입니다. 이 때문에 고정된 인공적 경계 조건 대신 0D 모델이 3D 모델에 경계 조건을 제공하므로 혈류는 저항 변화에 맞추어 적응적으로 변화할 것입니다. Figure 5에서 보여지는 것처럼 이는 경계 조건을 수동으로 제공하는 불확실성을 회피하기 때문에 뇌동맥의 폐쇄루프 기하학적 다중척도 모델을 사용할 필요성을 필요로 합니다.
>> TCD로 측정된 좌우 내경동맥과 뇌기저동맥의 유속 결과를 목표로 하여, 개인 맞춤형 집적 매개변수 모델의 매개변수를 최적화하고 조정했습니다. 계산 결과와 임상 측정 결과 간의 일치를 바탕으로, 본 연구에서 3D 모델에 제공된 비고정 경계 조건이 두 자원자의 실제 생리적 상태와 일치함을 입증하였습니다. 이 경계 조건은 다양한 협착 모델의 혈역학적 계산을 수립하는 기준으로 사용되었습니다.
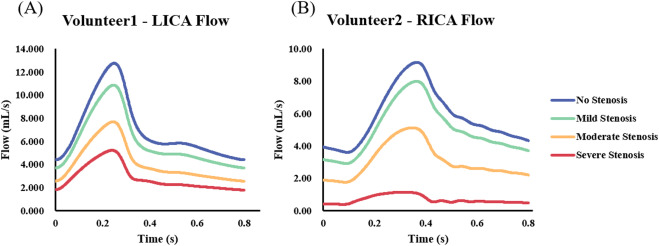
4.2. Hemodynamic effects arising from different ICA stenosis severities

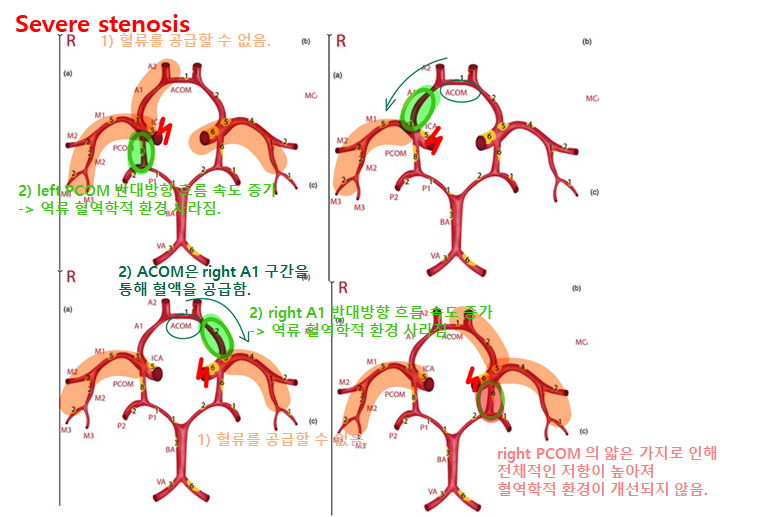
4.3. Volunteers difference
- Volunteer 1의 PCOM 은 Volunteer 2 의 2배였음. 따라서 Volunteer 2 의 PCOM 혈류 속도는 Volunteer 1에 비해 작았음. Volunteer 2의 LICA 에 중증 협착이 발생하면, left PCOM 에서 낮은 TAWSS 와 높은 OSI 의 혈역학적 변화가 발생했을 것임.
- 두 Volunteers 의 CoW 의 해부학적 구조가 다르기 때문에 ICA stenosis 가 발생하면 3D 모델에서의 혈역학적 변화가 다름. Volunteer 1의 경우 RICA stenosis 는 right A1 segment of the ACA 에서 혈역학적 변화를 일으킬 것임. Volnteer 2의 경우 LICA stenosis 가 발생하면 left A1 segment of the ACA 에서 혈역학적 변화를 일으킬 것임.
- Volunteer 1의 총 뇌동맥 혈류는 0.92 mL/s 더 컸지만, Volunteer 2의 기저동맥 (BA) 혈류는 1.2 mL/s 더 컸음. Volunteer 1은 ICA 혈류가 더컸기 때문에 ICA 가 협착되었을 때 CoW 혈역학적 변화가 더욱 분명했음. Volunteer 2의 BA 혈류가 더 크기 때문에 PCOM 보상 혈류율 및 혈류 속도가 낮았음.
4.4. Clinical proof
- (A1 segment of the ACA 협착을 동반한 ICA 협착) 4년 동안 좌측 사지에 일시적인 운동 약화와 감각 저하를 종종 경험. 일시적인 신경학적 결손 빈도 (her transient neurological deficits) 가 시간이 지남에 따라 증가함.
>> Cerebral angiograms showed stenoses of the left distal internal carotid artery, the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery, the A1 segment of the left anterior cerebral artery, and the P1 segment of the right posterior cerebral artery.
- (PCOM 협착을 동반한 ICA 협착) 오른쪽 사지에 일시적인 운동 약화와 감각 저하를 여러 번 경험.
>> Cerebral angiography showed stenoses in the distal internal carotid arteries and the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery, as well as occlusion of the right posterior communicating cerebral artery. Net-like collateral vessels were not evident.
- (left PCOM 협착을 동반한 LICA 협착) 다른 환자는 6개월 동안 episodic 오른쪽 사지 약화와 함께 오른쪽 시야 상실을 보였고, 1개월 동안 악화되었음. 뇌혈관조영술에서 occlusion of the LICA, dilating of the ACA, insufficient visualization of the left middle artery, and severe stenosis of the left PCOM near the ICA.이 확인되었음. left PCOM 재혈관화 (revascularization) 후 허혈 증상 사라지고 정상 생활 영위.
따라서, CoW 협착을 동반한 ICA 협착증 환자가 많고 재혈관화를 통한 CoW 치료는 혈류 보상을 개선할 수 있음.

